Ultraviolet LIdar for Canopy Experiment
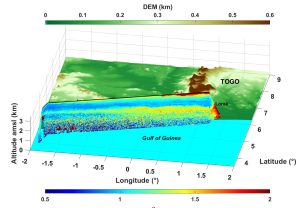
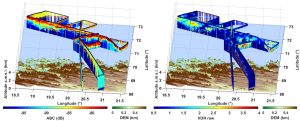
ULICE is a lidar initially developed for the study of forests from aircraft. It operates in the UV with a large ground footprint. ULICE was also used on board the ATR-42 to study aerosols over the Gulf of Guinea during DACCIWA (Dynamics-aerosol-chemistry-cloud interactions in West Africa) in July 2016 and to study clouds during ISLAS in March 2022.




References
Shang, X. and Chazette, P. (2015), End-to-End Simulation for a Forest-Dedicated Full-Waveform Lidar Onboard a Satellite Initialized from Airborne Ultraviolet Lidar Experiments, Remote Sensing, 7(5), 5222-5255; doi:10.3390/rs70505222.
Shang, X., Chazette, P., Totems, J., Dieudonné, E., Hamonou, E., Duflot, V., Strasberg, D., Flores, O., Fournel, J., Tulet, P.: Tropical Forests of Réunion Island Classified from Airborne Full-Waveform LiDAR Measurements. Remote Sens. 8, 43. doi:10.3390/rs8010043, 2016.
Flamant, C., Deroubaix, A., Chazette, P., Brito, J., Gaetani, M., Knippertz, P., Fink, A. H., de Coetlogon, G., Menut, L., Colomb, A., Denjean, C., Meynadier, R., Rosenberg, P., Dupuy, R., Dominutti, P., Duplissy, J., Bourrianne, T., Schwarzenboeck, A., Ramonet, M., and Totems, J.: Aerosol distribution in the northern Gulf of Guinea: local anthropogenic sources, long-range transport, and the role of coastal shallow circulations, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 18, 12363-12389, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-12363-2018, 2018.
